- 15th Oct, 2024
- Abdominal Doctor
Excess Stomach Fat: A Cause Of Abdominal Pain
Abdominal pain is a common gastrointestinal issue that people experience at some point in their lives. It can stem from a variety of causes, including poor diet, digestive problems, or other GI disorders. Stomach aches that result from gas, acidity, or nausea usually go away on their own or by taking medicines like antacids. However, if the pain persists for more than 48 hours, it indicates several other complications.
In that case, an abdominal pain doctor usually recommends certain tests to know the cause of the discomfort. But sometimes, the reports come back as normal, due to which it becomes extremely difficult to diagnose the condition.
What most people ignore is that their lifestyle choices, including excess abdominal fat or obesity, are a major contributing factor behind the severe aches and discomfort in the abdomen.
In this blog, we will delve deeper to understand how stomach fat is related to abdominal pain and what the strategies are to manage the condition.
Understanding Abdominal Fat
Stomach fat, better known as visceral fat, usually gets deposited beneath the abdomen and surrounds the vital organs like the kidneys, liver and intestines. Unlike subcutaneous fat, which is stored beneath the skin, visceral fat is a key player in a variety of health problems.
What’s The Link Between Stomach Fat And Abdominal Pain?
Here are the ways excessive abdominal fat leads to pain and discomfort in the stomach in several ways, explains Dr. Indraneel Saha, a trusted abdominal pain doctor.
- Inflammation: Visceral fat contributes to chronic inflammation disorders in the body, especially in the abdomen, causing pain and discomfort.
- Increased pressure on the organs: As abdominal fat surrounds the organs, it puts immense pressure on the stomach, pancreas, liver and small intestine, leading to bloating and pain.
- Digestive issues: Obese patients are more likely to have digestive issues as compared to those who have a normal BMI. Obesity is the leading cause of the formation of gallstones, bloating, nausea, constipation and vomiting.
- GERD: Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is more common in individuals who have abdominal or visceral fat deposition over the years. This is because the extra fat around the belly squeezes the stomach, allowing the stomach’s acidic content to flow back into the esophagus. Pain in the upper abdomen along with a burning sensation in the heart is a symptom of GERD.
- Metabolic syndromes: Visceral fat is linked to metabolic syndromes like insulin resistance and diverticulosis which affects the gut health and causes pain in the lower abdominal pain, tenderness, fever and bloating.
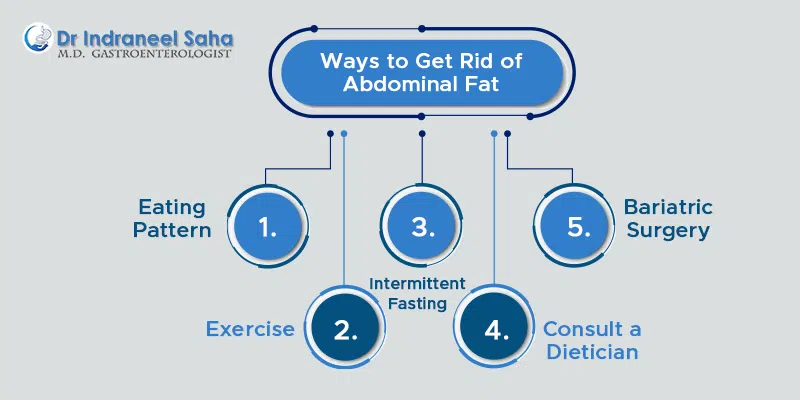
Ways To Get Rid Of Abdominal Fat
The best way to deal with visceral fat is to adopt a healthy diet and lifestyle choices. Below are the habits that you must inculcate in your daily routine.
- Eating pattern: Focus on a diet that includes plant-based items like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, beans, legumes, nuts, seeds and low-fat dairy products.
- Exercise: Engage in aerobic exercises like running, jogging, cycling, swimming and stair climbing. You can even do training with weights to burn calories and strengthen the muscles.
- Intermittent fasting: You can do intermittent fasting, which involves eating and no eating patterns.
- Consult a dietician: If required, contact a professional nutritionist who will prepare a diet chart based on your needs.
- Bariatric surgery: If exercise and diet do not show any results, fat removal surgery is the last resort to shed the weight kilos.
 Conclusion
Conclusion
If you are experiencing chronic stomach pain, talk to an abdominal pain doctor to find out the cause of the discomfort. In the meantime, also ensure to just take a break from unhealthy foods and sedentary life and give your body a chance to adjust to the new routine.