Endoscopic Intervention
What Is Esophageal Stenting?
Esophageal stenting, also known as esophageal stent placement or esophageal stent insertion, is a medical procedure used to treat narrowing or blockage of the esophagus. This narrowing can be caused by various conditions such as esophageal cancer, strictures (scar tissue), or external compression from nearby structures.
Why Is Esophageal Stenting Performed?
- Relief of Dysphagia: It helps alleviate difficulty swallowing caused by conditions such as esophageal cancer, strictures, or external compression.
- Palliative Care: Esophageal stenting can improve quality of life for patients with advanced esophageal cancer by providing relief from symptoms such as dysphagia and pain.
- Treatment of Benign Conditions: Stenting may be used to treat benign esophageal strictures that have not responded to other treatments.
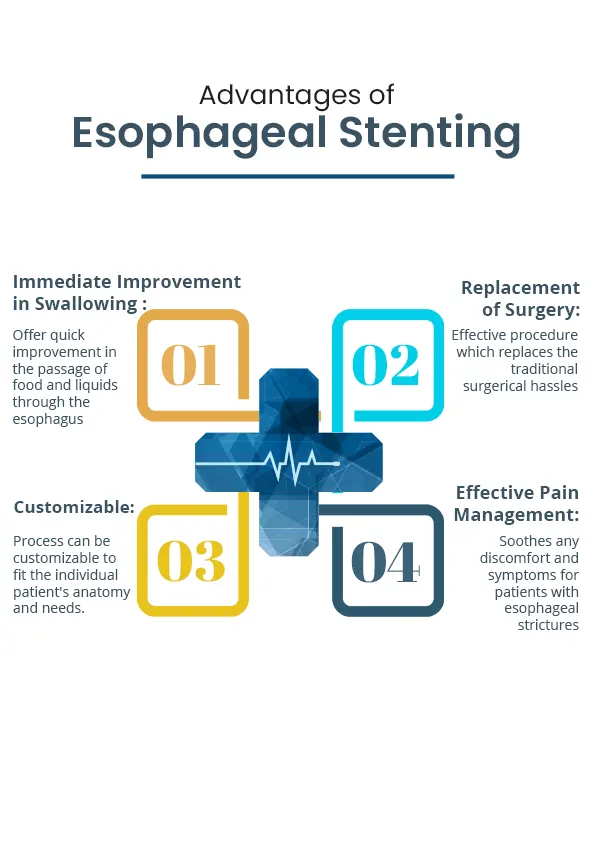
Advantages of Esophageal Stenting
- Replacement to Surgery: In some cases, esophageal stenting may be an alternative to surgery for treating esophageal strictures or cancer, particularly in patients who are not candidates for surgery due to medical reasons.
- Immediate Relief: Symptoms often improve rapidly following stent placement, providing immediate relief to patients experiencing swallowing difficulties.
- Minimal Invasiveness: It is a minimally invasive procedure that can often be performed without the need for open surgery, reducing recovery time and risk of complications.