- 20th May, 2025
- Esophageal Dilatation
Dietary Guidelines for Patients with Esophageal Strictures
Do you often feel something is stuck in your throat or chest? This may be due to abnormal narrowing of the esophagus (swallowing tube). This narrowing makes it difficult for food to pass through the esophagus. Some of the other symptoms which an individual might experience are pain, choking and coughing when swallowing.
For such patients, eating certain foods or maintaining certain guidelines is necessary to make eating easier and digestible.
The main goal of resorting to dietary precautions is to make eating less painful and prevent the food from lingering in the esophagus, which can cause irritation and further narrowing.
In this blog, we will list the food items and dietary strategies for patients with esophageal strictures.
Esophageal Strictures: An Overview
Esophageal strictures are a medical condition that is characterised by abnormal narrowing of the esophagus( the tube that carries food from the mouth to the stomach).
An individual suffering from esophageal strictures finds it hard to swallow food, a condition known as dysphagia. They often have the feeling that food is getting stuck in the throat. Esophageal strictures result from a variety of factors, such as persistent inflammation, chronic acid reflux (GERD), radiation therapy and even injuries.
For most esophageal strictures, esophageal dilatation is the most effective treatment method to widen the area to a larger size.
How is Esophageal Dilatation Carried Out?
During esophageal dilatation, an endoscope is inserted into the mouth and passed through the esophagus to visualise the area that needs dilatation. A deflation balloon catheter is also inserted and advanced to the narrowed area. Once in place, the balloon is inflated to stretch and widen the esophagus.
Esophageal dilatation is a completely safe procedure where patients are sedated to help them relax and minimise discomfort. It is an outpatient procedure, and patients are discharged on the same day.
Why Dietary Restrictions Matter for Patients with Esophageal Strictures
When the esophagus gets narrowed, dry or coarse, the food becomes lodged in the esophagus and causes further irritation. Hence, adopting a healthy eating pattern is important to prevent further complications in the esophagus. Here are some of the reasons behind it:
- Minimising irritation, inflammation and strain
- Reducing pain during swallowing
- Prevent food from getting stuck
- Promote healing after esophageal dilatation
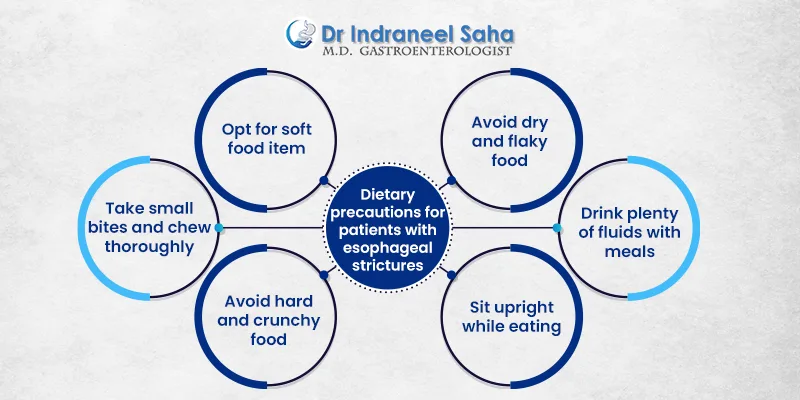
Dietary Precautions for Patients with Esophageal Strictures
Here are the dietary guidelines that patients with esophageal strictures must follow.
Opt for soft food items
Soft, moist and chewable foods are the safest for patients with esophageal strictures. Some examples include soups, broths, smashed potatoes, tender vegetables, scrambled eggs, well-cooked cereals and yoghurt.
Take small bites and chew thoroughly
You can manage esophageal strictures by taking small bites and chewing thoroughly until it’s almost liquid. Eating too quickly can cause choking.
Avoid hard and crunchy food
Make sure to avoid hard and crunchy foods like raw vegetables, whole fruits, popcorn, sticky pasta, nuts and chips as they can irritate the esophageal lining or get stuck.
Avoid dry and flaky food
Patients with esophageal strictures limit the consumption of dry and flaky items such as crackers, hard bread and certain cereals as they make swallowing difficult.
Drink plenty of fluids with meals
Drinking sips of water while having meals moistens the food and ensures that the food passes through the esophagus quite easily without getting stuck. However, avoid drinking caffeine, carbonated beverages and alcohol.
Sit upright while eating
Posture plays an important role in preventing acid reflux. Make sure you sit upright while eating and remain at least for 40-45 minutes afterwards.
Post-Esophagal Dilatation Meals
Following esophageal dilatation, patients are also required to stick to dietary precautions. Here they are:
Clear liquids: Immediately after the procedure, stick to a clear liquid diet to ease digestion and allow the esophagus to heal.
Full liquids: After 48 hours following the procedure, patients can gradually progress to having milk, smoothies and curd.
Soft diet: Within 4-5 days, one can introduce soft food items like pureed potatoes, cooked vegetables and fruits without skin in their diet upon doctor’s instructions.
Foods to Avoid in Esophageal Strictures
Here are the following items which need to be avoided if you have esophageal strictures.
- Acidic foods like lemons, limes, oranges and tomatoes.
- Spicy and processed food
- Carbonated drinks
- Alcohol
- High-fat food
- Caffeine
- Chocolate
- Peppermint
- Food that soothes the esophagus
These food items are known to give relief from esophageal strictures and even promote healing after esophageal dilatation.
- Fruits like bananas and watermelons
- Properly cooked vegetables like carrots, spinach and pumpkin
- Starches like oatmeal and whole-grain bread
- Lean protein such as tofu, chicken and egg whites
- Dairy products like milk and yoghurt
- Drinks like Herbal teas
- Eating habits to consider
Besides following the dietary precautions, there are certain eating habits that patients must take note of
- Lying down immediately after eating
- Eating heavy meals, especially at night
- Wearing tight clothes while eating
- These habits lead to acid reflux and worsen esophageal strictures
- Lifestyle changes consideration
Living with esophageal strictures requires long-term lifestyle management. Here are some of the strategies:
- Eating small and frequent meals
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Regular follow-ups are needed to find out any changes in the symptoms.
Final words
Esophageal strictures are a serious condition that interferes with the quality of life. While medical procedures like esophageal dilatation provide relief, dietary management is also necessary for long-term comfort and to prevent complications.